8 Facts You Should Know to Prevent Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
Carbon monoxide is more commonly thought of as a deadly poison in the winter. But it’s often the culprit of many incidents during other seasons as well. You probably know that when you use a gas or wood-burning appliance, such as a furnace, you increase the risk of carbon-monoxide (CO) poisoning. However, other appliances and equipment, such as a gas oven, stove or water heater can also produce CO.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, at least 430 people die each year from accidental carbon monoxide poisoning. Additionally, more than 4,000 Americans are hospitalized each year for CO poisoning and more than 100,000 people get sick enough from exposure to visit the ER.
Reading these statistics you might think, “How then do I prevent from getting carbon monoxide poisoning?” After all, most homes’ heating systems use gas or wood as their fuel source. To help answer that question, we’ve come up with a list of 8 Facts You Should Know to Prevent Carbon Monoxide Poisoning. These facts should help you understand the dangers of CO and how to stay safe.
1. Carbon monoxide poisoning is hard to detect.
Carbon monoxide, often referred to as CO, is an odorless and tasteless gas that’s invisible to the eye. It does not have any easily identified characteristics. Therefore, an unsuspecting person has no way of sensing they are in danger if a home or office building has dangerous levels of CO.
2. CO and CO2 are very different.
The “C” and “O”, which make up the chemical formula for carbon monoxide, refer to one carbon molecule and one oxygen molecule. Compare this to carbon dioxide (CO2), which has two oxygen molecules. CO2 is a gas that humans manufacture and exhale during normal respiration, and is not toxic.
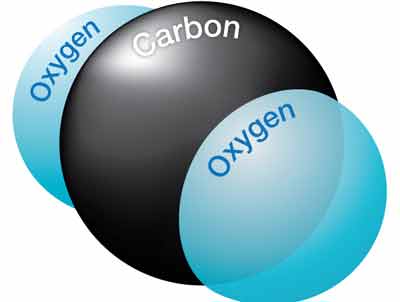
3. Carbon monoxide is always present when burning fuels.
CO is formed when a fuel is burned incompletely. Complete combustion is only possible in a laboratory situation; therefore, in the real world, combustion is always incomplete. This means that some level of carbon monoxide is always present during the burning of fuels. The key is to keep the level of CO to a minimum by maintaining proper combustion and flue venting.

4. Carbon monoxide poisoning can occur from many different scenarios.
Dangerous levels can develop very slowly over several days. In some cases, life-threatening levels of CO can occur in mere minutes. Each scenario is different, depending on the gas or wood-burning equipment used in the building.
5. Any fuel or wood-burning appliance or equipment can cause CO poisoning.
Those appliances or equipment that could be culprits to CO poisoning are gas or wood-burning water heaters, stoves, ovens, furnaces and boilers. They can be responsible for elevated CO levels in the home, an office building or a hotel.
Cars and trucks never achieve complete combustion, and so even the best-tuned vehicle is always going to produce some carbon monoxide.

Image Source: Art of Gears
6. Symptoms of CO poisoning can mimic the flu.
At even low levels of CO exposure, the most common symptoms of poisoning are often mistaken for the flu–headache, dizziness, nausea and weakness. When levels of exposure are higher, symptoms include shortness of breath, chest pain, vomiting, blurred vision and loss of consciousness.
If you believe you are experiencing symptoms of CO poisoning, go outside and get fresh air immediately and call the fire department.

Image Source:Dizzy Day Clinics
7. You can help prevent CO poisoning by installing a CO detector and getting an annual furnace check up.
One of the easiest ways to stay safe is to invest in a CO detector. Depending on the building code in your area, enclosed garages for condos, apartments, stores and offices are required to have automatic CO detectors and fan controls. New homes with attached garages typically are required to have CO detectors.
Another way to help prevent poisoning is to have your furnace or heating system inspected each year. Add to that list any water heaters or other gas or wood-burning appliance, including chimneys and flues.

Image Source: Fox10 TV
8. You shouldn’t operate portable fuel burning appliances indoors.
These include portable generators and other gas-powered tools. Some other don’ts include using charcoal inside your house, garage, vehicle or tent. And maybe one you don’t think about–don’t leave a car running in an attached garage, even if the door is open.
Wondering if there are other appliances or objects that can cause CO poisoning? Read this list of common causes of CO poisoning.

How many of these facts about carbon monoxide did you already know? Hopefully there were a few that may help you avoid a CO poisoning incident. And remember Ivey Engineering when you’re in need of a carbon-monoxide expert.












